The Threat of Office Macros
While many organizations depend on Microsoft Office macros for business-critical processes, they pose a high risk for IT security. Macros are programs within Office documents that execute with the same permissions as the user opening the document. Not to speak of macros that use other exploits to elevate their privileges even beyond that. That makes Office macros a preferred way for hackers to get into organizations, with attacks ranging from ransomware to spear phishing.
Unlike normal programs, Office documents are often opened by users without thinking twice. Enabling macro execution is then just a click away, which is especially easy to achieve via social engineering by including instructions in an email or even the document itself.
Also unlike normal programs, administrators find it almost impossible to provide policy settings that define which macros may be executed. Policy frameworks such as application control/whitelisting don’t work for macros. And malware scanners will always miss some malevolent macros.
Implement Macro Signing to Create Secure End User Policies
Digitally signing your organization’s macros will unlock the policy capabilities of Microsoft Office:
- Use group policies to allow execution only for macros signed with trusted certificates
- Assign trusted certificates to users and groups

Using SignPath, you can keep your signing keys safe and easily create well-defined signing processes for each of these certificates.
Inadequacy of Existing Approaches
This table shows how readily available policies provide inadequate security and/or impact the business to an unacceptable degree:
| Method | Security level | Implementation | Business impact | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enable macro execution | 🔴 | 🟢 | 🟢 | This should never be enabled |
| Let users decide whether to execute macros | 🟠 | 🟢 | 🟢 | You cannot rely on users always making the right decision |
| Disable macro execution except for digitally signed macros | 🟡 | 🟠 | 🟢 | Digital signing in Office is a manual activity and requires private key access for macro authors from their development PCs |
| Disable macro execution except for users who require them | 🟡 | 🔴 | 🟠 | Each of these users still poses a risk, and they often add up |
| Disable macro execution except for certain storage locations | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 | This will mitigate direct internet/email attacks, but still any user can drop a malicious document in a trusted location |
| Disable macro execution for everyone | 🟢 | 🟢 | 🔴 | Very safe but often unrealistic |
| Using SignPath: Disable macro execution except for digitally signed macros |
🟢 | 🟢 | 🟢 | Provide a secure process that aligns signing authorization and approval policies with macro execution policies. |
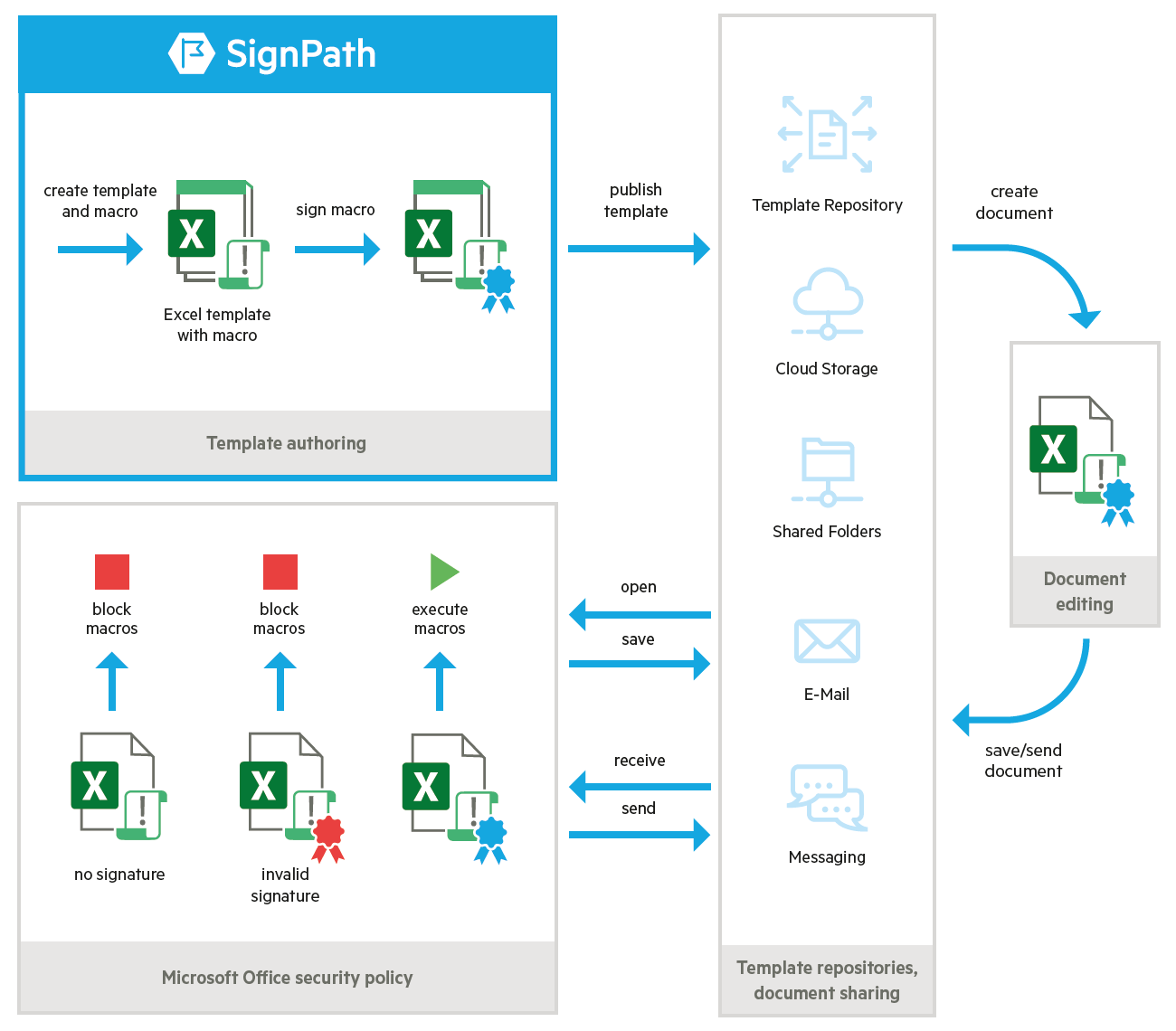
End-to-End Security for Office Macros
Macros signing is easy to set up using the policy framework provided by SignPath:
- VBA developers create and edit macros in office documents and document templates
- Macros are signed manually or automatically using SignPath
- Administrators set up signing permissions and approval rules
For approved macros, this process has no impact on business units using Office documents:
- Users can create new documents and view, edit and save data in existing documents without affecting signed macros
- Documents can be stored in any location and shared via email
Certificate scopes: global vs. departmental execution permissions
Once you have set up a signing policy for your organization, you can disable execution of unsigned macros via Microsoft Office group policies.
Fine-tune signing and execution permissions
Some organizations need more fine-grained control over macro execution. In this case you can assign specific macro signing certificates to departments.
| Department | Trusted certificates |
|---|---|
| Finance | Global, Finance |
| Legal | Legal |
| Engineering | Global, Engineering, some subcontractors |
| Restricted users | none |
| Everyone else | Global |
Adjust your signing policies accordingly, e.g. provide signing permissions for the Finance certificate only to macro authors supposed to create Office macros for the finance departement.
Business partners and customers
For documents that are used outside of your organization, you can use your EV code signing certificate. External users, such as business partners or customers, will be informed that macros have been signed by your organizations. They can then decide to trust these macros on a per-user basis or through their own policy framework.